Luke Ericson is tough as nails.
Human gait is cyclical. For the most part, when one limb is engaged on the ground (stance phase), the other is in swing phase. Before I continue, you should recall that there is a brief double limb support phase in walking gait, that which is absent in running gait. Also, I wish to remind you of our time hammered principle that when the foot is on the ground the glutes are heavily in charge, and when the foot is in the air, the abdominals are heavily in charge.
For one to move cleanly and efficiently one would assume that the best way to do that would be to ensure that the lower 2 limbs are capable of doing the exact same things, with the same timing, same skill, same endurance and same strength. This goes for the upper 2 limbs as well, and then of course the synchronizing of the 4 in a cohesive effort. For this clean seamless motor function to occur, one must assume that there would be no injuries that had left a remnant mark on one limb thus encouraging a necessary compensation pattern in that limb (and one that would then have to be negotiated with the opposite limb as well as the contralateral upper or lower limb).
Removing a considerable mass of tissue anywhere in the body is going to change the symmetry of the body and require compensations. One can clearly see the effects of this on this athletes body in the video above. He even eludes to the fact that he has a scoliosis, no surprise there. There is such an unequal mass distribution that there is little way the spine had any chance to remain straight. Not only is this going to change symmetry from a static postural perspective (bulk, weight, fascial plane changes, strength etc) but it will change dynamic postural control, mobility and stability as well as dynamic spinal kinematics. I have talked about this previously in a blog piece I wrote on post-mastectomy clients display changes in spatiotemporal gait parameter such as step length and gait velocity.
-mastectomy post: http://tmblr.co/ZrRYjx1XB8RhO
If you have been with The Gait Guys for awhile you will know that impairing an arm swing will show altered biomechanics in the opposite lower limb (and furthermore, if you alter one lower limb, you begin a process of altering the biomechanical function and rhythmicity of the opposite leg as well.) You can search the blog for “arm swing part 1 and part 2″ for those dialogues.
Arm swing impairment is a real issue and it is one that is typically far overlooked and misrepresented. The intrinsic effects of altering the body through subtraction of tissue are not all that dissimilar to extrinsic changes into the system from things like walking with a handbag/briefcase, walking with a shoulder bag, walking and running with an ipod or water bottle in one hand. And do not forget other intrinsic problems that affect spinal symmetry, for example consider the changes on the system from scoliosis as in this case. It can cycle back on its own feedback loop into the system, either consciously or unconsciously altering arm swing and thus global body kinematics.
There is a reason that in our practices we often assess and treat contralateral upper and lower limbs as well as to address remnants from old injuries whether they are symptomatic or not. It all comes together for the organism as a concerted effort in optimal locomotion.
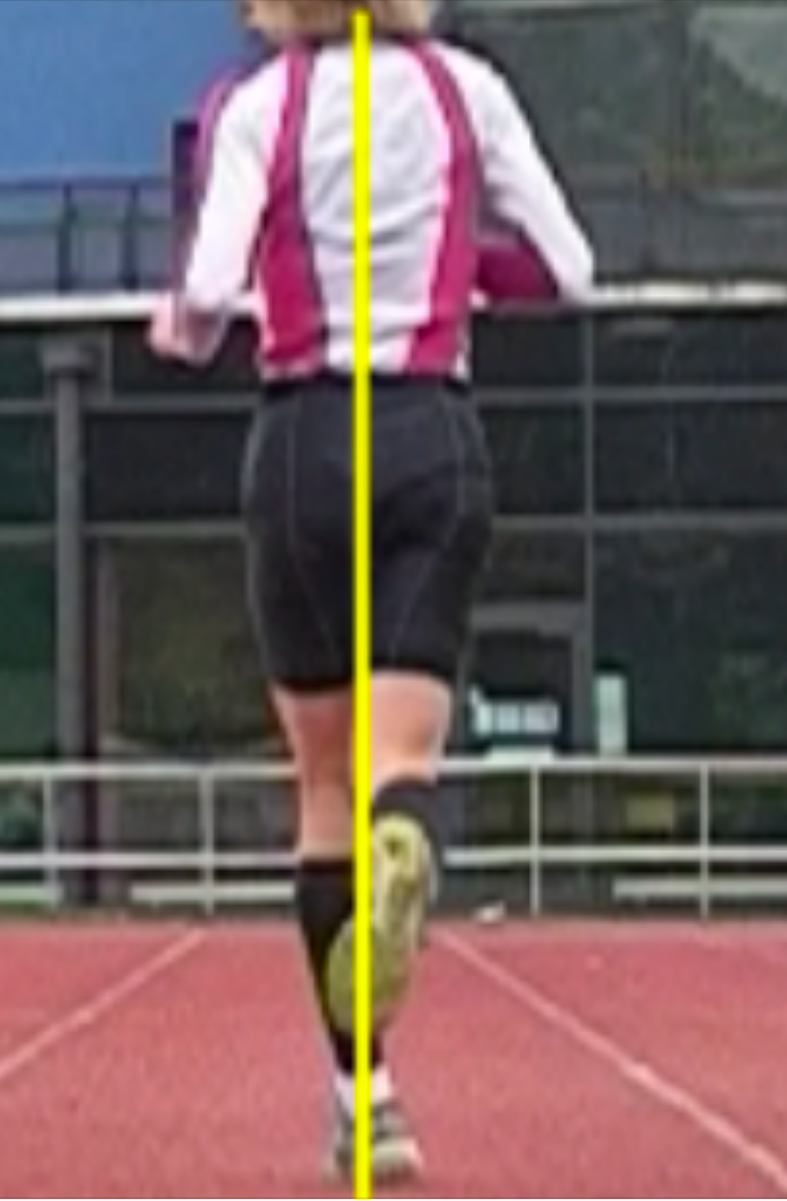
Here on TGG, and in dialogues with Ivo on our podcast, I have long talked about phasic and anti-phasic motions of the arms and shoulder-pelvic blocks during gait and locomotion/sport activity. I have written several times about the effects of spine pain and how spine pain clients reduce the anti-phasic rotational (axial) nature of the shoulder girdle and pelvic girdle. In the video above, you can see anything but anti-phasic gait, to be clear, this is a classic representation of a phasic gait. The shoulder block and the pelvic block show little if any counter rotation, they are linked together which is not normal gait. Furthermore, if you look carefully, the timing of the right arm swing is variable and cyclically changing in its timing with the left leg. Look carefully, you will see the cyclical success and failure at the beginning of the video. This is pathologic gait, he must be constantly fighting frontal plane sway because there is no axial anti-phasic motion. He is also constantly fighting the unidirectional rotation that the absence of an entire limb and limb girdle is presenting, you can see him struggle with this if you have looked at enough gait samplings. There is essentially frozen torso movements. Want to see more of our work on arm swing ? search the gait guys blog.
There is so much more here to discuss, so I will likely return to this video another time to delve into those other things on my mind. Luke is an amazing athlete, he gets much respect from me.
I hope this dialogue helps you to get a deeper grip on gait and gait problems. I have written many articles on the topics of arm swing, phasic and anti-phasic gait, central pattern generators. The are all archived here on the blog. I try to write a new original thought-process article each week for the blog amongst the other “aggregator” type stuff we share from other folks social media. My weekly article serves to go deeper into things, sometimes they are well referenced and in this case, I am basing today’s discussion on the referenced work in the other pieces I have written on arm swing, phasic and anti-phasic gait, central pattern generators etc. So please do your readings there before we begin debate or dialogue, which i always welcome !
Dr. Shawn Allen, the other gait guy