Part 2: The amputated hallux & the complex biomechanical fall-out from it.
/Last week we promised Part 2 to this case, the amputated big toe.
Here is part 2. These are the complicated biomechanical fall-outs, so grab a big mug o' coffee and have at it !
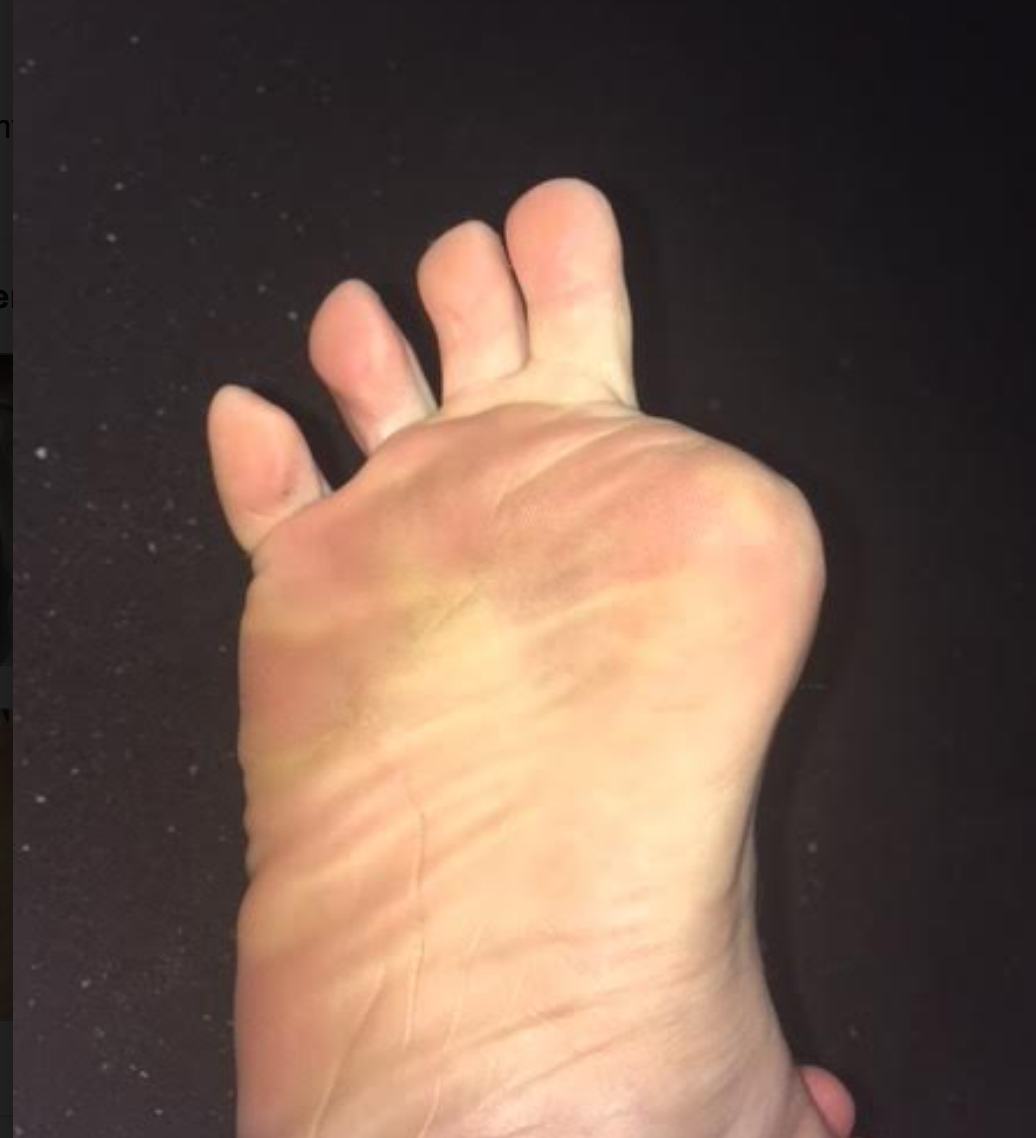
In review, this person (all photos and case premissioned in swap for insight) had the distal hallux removed because of a progressive melanoma on the big toe. Can you believe that ! This is one more reminder that the sun and regular dermatologist screenings are wise.
This person had a complaint of progressing right gluteal and QL pain, spasm, tone and some persistent pain now in the 2nd metatarsal as well as some shoe challenges. We discuss this case briefly in and upcoming podcast, #139 or #140 we believe.
Before we add our final thoughts to this case, lets cap our post from last week.
-Without the hallux, we cannot wind up the windlass and shorten the distance between the first metatarsal and heel, thus the arch will splay (more permanently over time we suspect) and we cannot optimize the arch height.
This will promote more internal spin on that limb because of more midfoot pronation and poor medial foot tripod stabilization.
- More internal limb spin means more internal hip spin, and more demand (which might not be met at the glute level) and thus loads that are supposed to be buffered with hip stabilization, will likely be transferred into the low back, and or into the medial knee. Look for more quad protective tone if they cannot get it from the glutes. Troubles arise when we try to control the hip from quadriceps strategies, it is poorly postured to do so, but people do it everyday, *hint: most cyclists and distance runners to a large degree).
- anterior pelvis posturing on the right, perhaps challenging durability of the lower abdominals, hence suspect QL increased protective tone, possible low back tightness or pain depending on duration of activities
- These factors are likely related to his complaints in the right gluteal and low back/QL area.
Now, onto our next thoughts.
- when the hallux is incompetent, in this case absent, there are few other choices to gain forefoot purchase on the ground other than more flexion gripping of the 2nd toe (then the 3rd, then 4th). This is a progressing "searching" phenomenon for forefoot stability and without the function of the big fella, the 2nd toe will begin a hammering phenomenon, often, but not always. We would not be surprised to see hammer toe development in this case, but this person is now very aware of it, and can at least now fight that battle with increased awareness. There is some mild evidence of this on the side lateral photo.
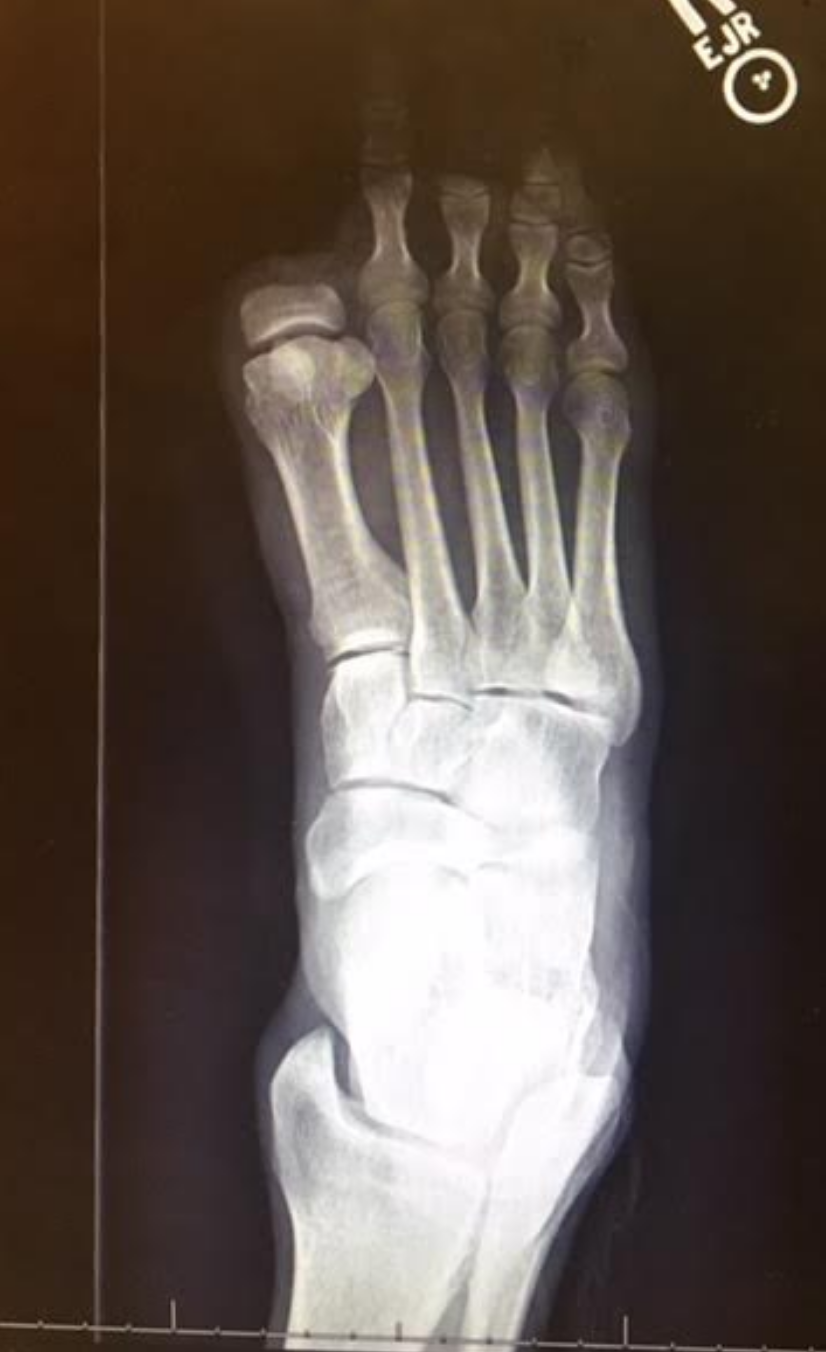
- We are happy to see that the proximal phalange was spared. The adductor hallucis is inserted medially there, and this will help to reduce bunion generation risk (medial metatarsal drift). Comparing the photo and the radiograph is a great example of how far back/proximal the 1st MTP joint is. One could easily assume that the entire hallux was resected from the photo, but the radiograph shows otherwise.
- Toe off is obviously going to be compromised. The patient cannot adequately stabilize the 1st metatarsal (MET) and this will mean a compromised foot tripod, medial foot/tripod splay, arch pronation control challenges but toe off stabilization is going to have to be met by the 2nd and 3rd digits, as discussed above. They are not suited to be the major players here, they are synergistic to this end. Do not be surprised to see one of 2 strategies at toe off here:
1. heavy medial foot tripod toe off, dropping into the void and this maximize the internal spin challenges and minimizing the requisite foot supination stiffness generation phase that should be normal at toe off
2. avoidance of the above, with a forced conscious forefoot lateral toe off, a supinatory strategy, to avoid internal limb spin, more toe hammering, and the lurch heavily and abruptly off of the right foot and onto the left limb.
3. taking #2 further, any time there is perceived challenges or deficits in strength, endurance, proprioception, balance, power and the like, the brain often will create a premature departure off of said limb, creating a requisite premature loading onto the opposite limb. This can cause a phenomenon well loosely refer to "catching" in the contralateral quadriceps mechanism. These clients, with their abrupt loading pattern onto the opposite limb will most often have troubles getting into initial gluteal hip stabilization strategies, and thus default into a quadriceps strategy, that in time can lead to quad shortness and increased tone, which can cause more compression across the patellofemoral joint and cause knee pain. This is more of a compression/loading response issue rather than tracking phenomenon, which we see at the typical diagnosis. We often look for causes in the opposite limb for contralateral knee pain. IT is quite often there if you are looking hard enough for it. Fix the problem, not the symptom.
There is a long host of other things than can arise from here, including heavy contralateral (in this case left sided) foot loading challenges, often more forefoot initial loading, and all of the problems than can arise when this pattern is cyclical, but that would take this post far too deep and long. So, . . . . another time.
4. Shoe fit, we could make the case that a shoe that nicely hugs the forefoot, as opposed to a wide toe box'ed shoe, could help fight off the risk of 1st metatarsal abduction and thus bunion formation risk. However, one cannot dismiss the wider toe box giving the remaining toes a better environment to engage without hammering with over use of long flexors. We might suggest a trial of an elastic sleeve, one often used for plantar fascitis symptom management, placing a snug one around the forefoot when ambulating. This could help keep that metatarsal snug and stop the bunion-like drift we would be watching for.
have at it gang, cases like this are far and deep and require deep understanding of normal and abnormal biomechanics, and the rabbit hole deep myriad of compensations that can be engaged.
have a great weekend !
Shawn and Ivo